How to create a Spring Boot Thymeleaf web application
In this article, I will be demonstrating creating a Spring Boot Thymeleaf web application.
Project Creation and Setup
Step 1 – Create a new Maven Project (Refer to this blog post). This should create a project as shown below:
Step 2 – Add the Spring Boot and Thymeleaf dependency. So, the pom.xml file should be similar to the following:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.learnjava</groupId> <artifactId>learnjava-springbootthymeleaf-demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies></project>
Writing Simple Code
Step 3 – Creating a Controller class
Let us first create a simple controller that displays a static html page without any data:
package com.learnjava.springbootthymeleafdemo.welcome;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controllerpublic class WelcomeController { @GetMapping("/") public String showHome() { return "home"; }}- The
WelcomeControllerclass has the @Controller annotation. This designates the class as an MVC controller. - It has a
showHomemethod. The GetMapping annotation specifies that this maps to the “/” path. - It simply returns the String hello. This specifies the name of the Thymeleaf template (an html file) that needs to be displayed.
Step 4 – Creating the Thymeleaf template file
As seen earlier, the controller returns the name of the Thymeleaf template. An HTML file with this name needs to be present in a templates folder within the src/main/resources folder. So, we need to create home.html within the src/main/resources/templates folder as follows:
<!DOCTYPE html><html> <head> <title>LearnJava Spring Boot Application</title> <link href = "css/style.css" rel = "stylesheet"/> </head> <body> <h2>Welcome to LearnJava!</h2> </body></html>
- This is a simple html file that displays a message
- It references the style.css.
Step 5 – Creating CSS file
The Thymeleaf template can optionally refer a CSS file as done above. In such cases, the specified CSS file needs to be present in a static folder within the src/main/resources folder. So, we need to create style.css within the src/main/resources/static folder as follows:
h2 { color: blue;}- This is a simple CSS file that displays H2 headings in blue colour.
Running the application
Step 6 – Run Main.java as a Java application as shown below:
Step 7 – Open http://localhost:8080/ in browser. This displays the following output:
Some More Code
Most real-world applications require to do more complex things than display a simple message. Let us write some more code that displays data in a tabular form.
Step 8 – Create a Book class as follows:
public class Book { private int id; private String name; private String author; // constructor, getters and setters}- The
Bookclass has fields corresponding toid,nameandauthor
Step 9 – Create a BookController class as follows:
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;@Controllerpublic class BookController { @Value("${greeting}") private String greeting; @GetMapping("/books") public String getAllBooks(Model model){ //Returns hardcoded data, a real world application would return from the database List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>(); books.add(new Book(1,"Emma", "Jane Austen")); books.add(new Book(2,"Harry Potter", "JK Rowling")); books.add(new Book(3,"The Partner", "John Grisham")); model.addAttribute("books", books); model.addAttribute("greeting",greeting); return "books"; } }- The
BookControllerclass has agreetingfield. It has the@Valueannotation with the value $greeting. This value can be set in the application.properties file as explained below. - The
BookControllerclass also has agetAllBooksmethod. This maps to the “/books” path as specified via the GetMapping annotation. - It accepts a Model object as a parameter. In Spring, A Model represents the data to be sent to the front-end.
- Next, the
getAllBooksmethod creates a List ofBookobjects and sets it as a Model attribute. In a typical Spring Boot application, data is retrieved via Spring Data JPA as demonstrated here. - Similarly, it also sets the
greetingfield as a Model attribute. - Thus, any data that needs to be sent to the HTML template, needs to be set as as model attribute like this.
- Finally, it returns the String books. This specifies the name of the Thymeleaf template.
Step 10 – Defining a greeting property
The BookController class has a greeting field. The @Value annotation assigns it a value via $greeting. Such properties need to be defined in an application.properties file within the src/main/resources folder. So, we need to create src/main/resources/application.properties as follows:
greeting=Hello!
Step 11 – Creating books.html
Just like home.html, we need to create books.html within the src/main/resources/templates folder as follows:
<html><head><title>Book</title></head><body><H2> <p th:text="${greeting}"></p></H2><table> <thead> <tr> <th>Book Id</th> <th>Book Name</th> <th>Book Author</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr th:each="book : ${books}"> <td th:text="${book.id}"></td> <td th:text="${book.name}"></td> <td th:text="${book.author}"></td> </tr> </tbody></table></body></html>- th:text is used to refer to the $greeting value
- th:each is used to iterate through the books list
- th:text is used to obtain the value of each book field
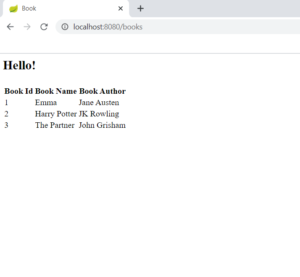
Step 12 – Run the application and type http://localhost:8080/books in a browser. This displays the following output:
You can download the complete source code from the GitHub Repository here.
Further Learning
Mastering Thymeleaf with Spring Boot
Spring Boot Tutorial for beginners
Spring Boot Fundamentals
Spring 5 with Spring Boot
Conclusion
So, in this article, we learnt how to create a simple Spring Boot Thymeleaf application.



Comments
Post a Comment